- Unit 1A: The Economizing Problem, International Trade and Finance
- Unit 1B: Supply & Demand
- Unit 2: Economic Indicators & the Businss Cycle
- Unit 3: National Income & Price Determination
- Unit 4: Financial Sector
- Unit 5: Long-Run Consequences of Stabilization Policies
- Unit 6: Open Economy: International Trade & Finance Revisted
AP Economics
Thanks for visiting the Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Page. Here you will find information, links, activities, tools, handouts, and objectives for each unit in AP Economics.
This site will continue to grow as I add new things, discover new links, and create items that will be useful for learning AP Economics.
This site primarily focuses on Macroeconomics - the branch of economics dedicated to the study of entire economic systems. In addition to preparing students for the AP Exam in May, my goal is for the students to gain the ability to analyze situations and choices by looking at the costs and benefits of decisions, both financially and practically.
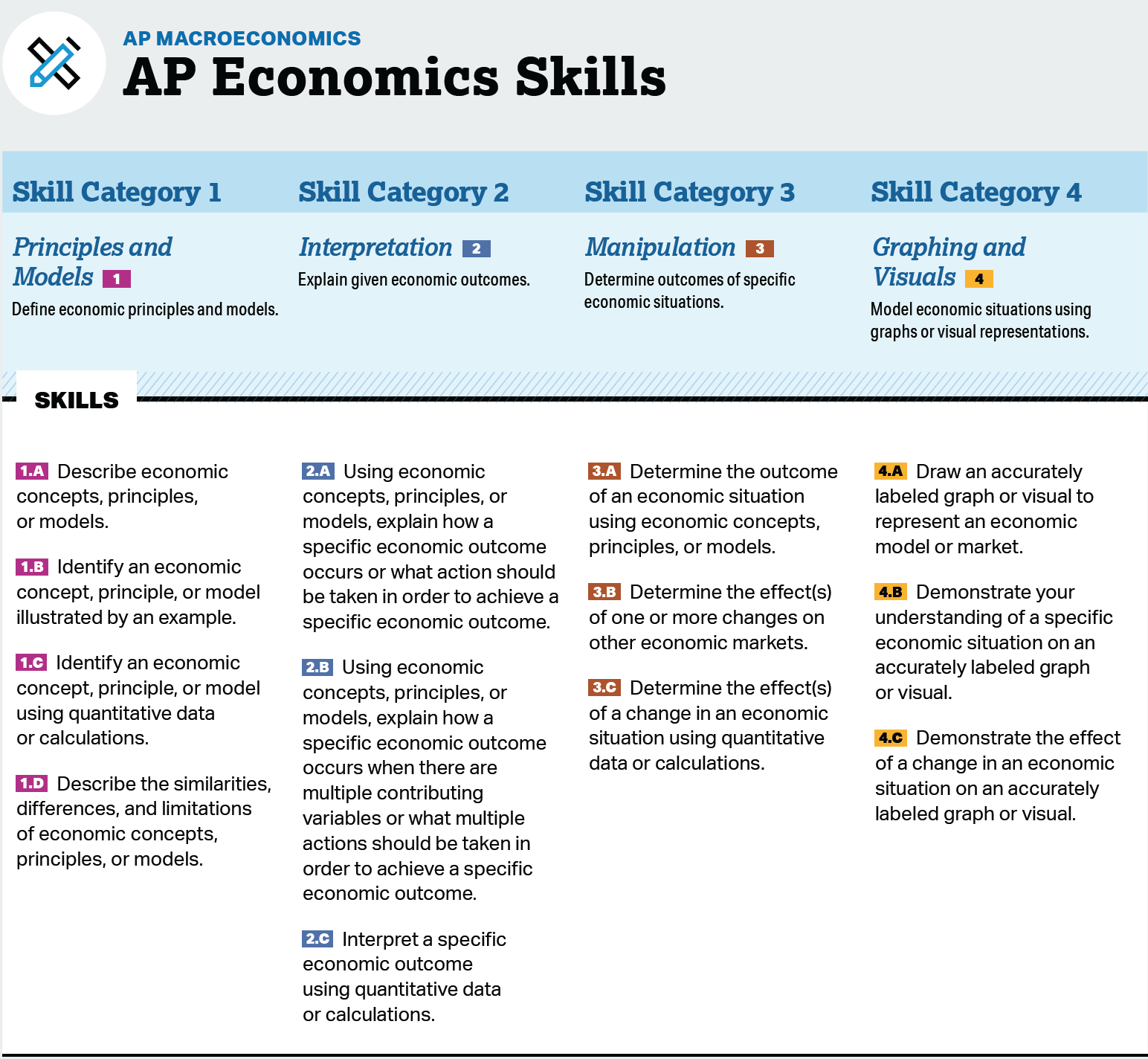
Countdown to AP ExamCourse Skills
The AP Economics skills describe what a student should be able to do while exploring course concepts. The table that follows presents these skills, which students should develop during the AP Macroeconomics course. These skills form the basis of the tasks on the AP Exam. The unit guides later in this publication embed and spiral these skills throughout the course, providing teachers with one way to integrate the skills in the course content with sufficient repetition to prepare students to transfer those skills when taking the AP Exam. Course content may be paired with a variety of skills on the AP Exam.
Course Content
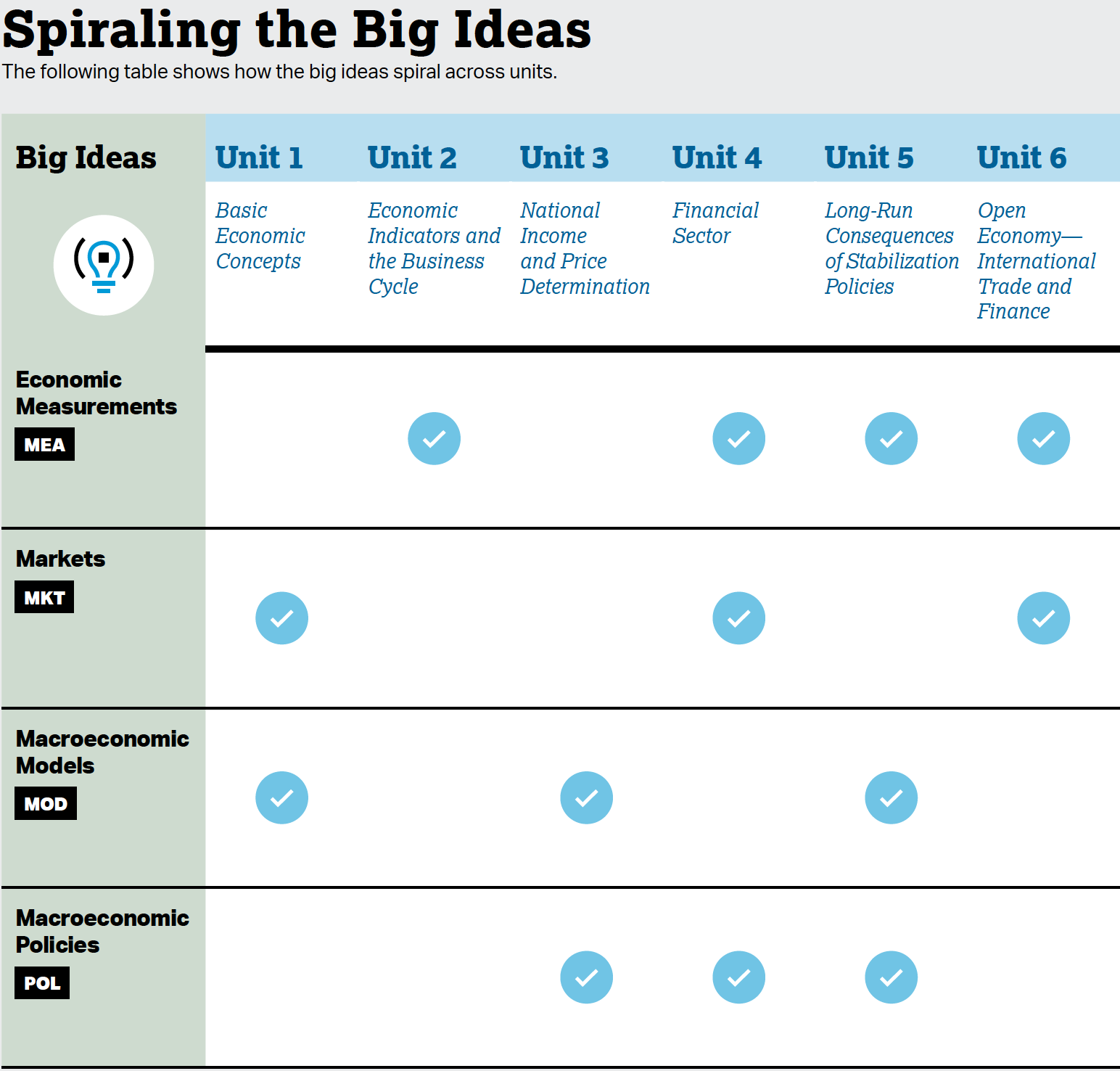
Big Ideas
The big ideas serve as the foundation of the course and allow students to create meaningful connections among concepts. They are often overarching concepts or themes that become threads that run throughout the course. Revisiting the big ideas and applying them in a variety of contexts allows students to develop deeper conceptual understanding. Below are the big ideas of the course and a brief description of each:
BIG IDEA 1: ECONOMIC MEASUREMENTS (MEA)
Economists construct measurements to monitor the state of an economy and evaluate its performance over time. Governments, firms, and citizens often use these measurements to help inform policy, business, and personal decisions.
BIG IDEA 2: MARKETS (MKT)
Competitive markets bring together buyers and sellers to exchange goods and services for mutual gain. The simple model of supply–demand can be applied in different market contexts.
BIG IDEA 3: MACROECONOMIC MODELS (MOD)
Macroeconomic models are simplified representations that depict basic economic relationships and can be used to predict and explain how those relationships are affected by economic shocks.
BIG IDEA 4: MACROECONOMIC POLICIES (POL)
Government taxation and spending policies and central bank monetary policy can affect an economy’s output, price level, and level of employment, both in the short run and in the long run.