Civics & Economicsby Matthew Caggia
- Semester 1 Bell Ringers
- Unit 1: Foundations of American Government
- Unit 2: The Constitution
- Unit 3A: Comparative Government- Legislative Branch
- Unit 3B: Comparative Government- Executive Branch
- Unit 3C: Comparative Government- Judicial Branch
- Unit 4A: Citizenship, Voting, & Elections
- Unit 4B: Political Parties & Influencing Government
- Unit 5: Making Laws
- Unit 6: Violating the Law
- Unit 7: Personal Financial Literacy
- Unit 8: Economic Fundamentals
- Unit 9: Government in the Economy
- Unit 10: International Economics
- Review Materials
- Landmark Supreme Court Cases
- Textbook
Unit 3B: Comparative Government - Executive Branch
Chapters 7, 13.2, 14.1&2
We now turn our attention to the Executive branch of government. We will investigate and analyze this law-enforcing part of government on three levels: Federal, State, and Local (County and Municipal). While the President is the face of the nation, and our representative to the world, the people of the United States turn to him as the leader of our nation. We will study the many different roles the president plays on a daily basis while he does his best to uphold the Constitution and carry out the laws passed by Congress.
We will also examine the role of the governor and the delicate balance between the needs of the people and how the state fits into the nation as a whole. As chief executive, the governor is our representative to other states.
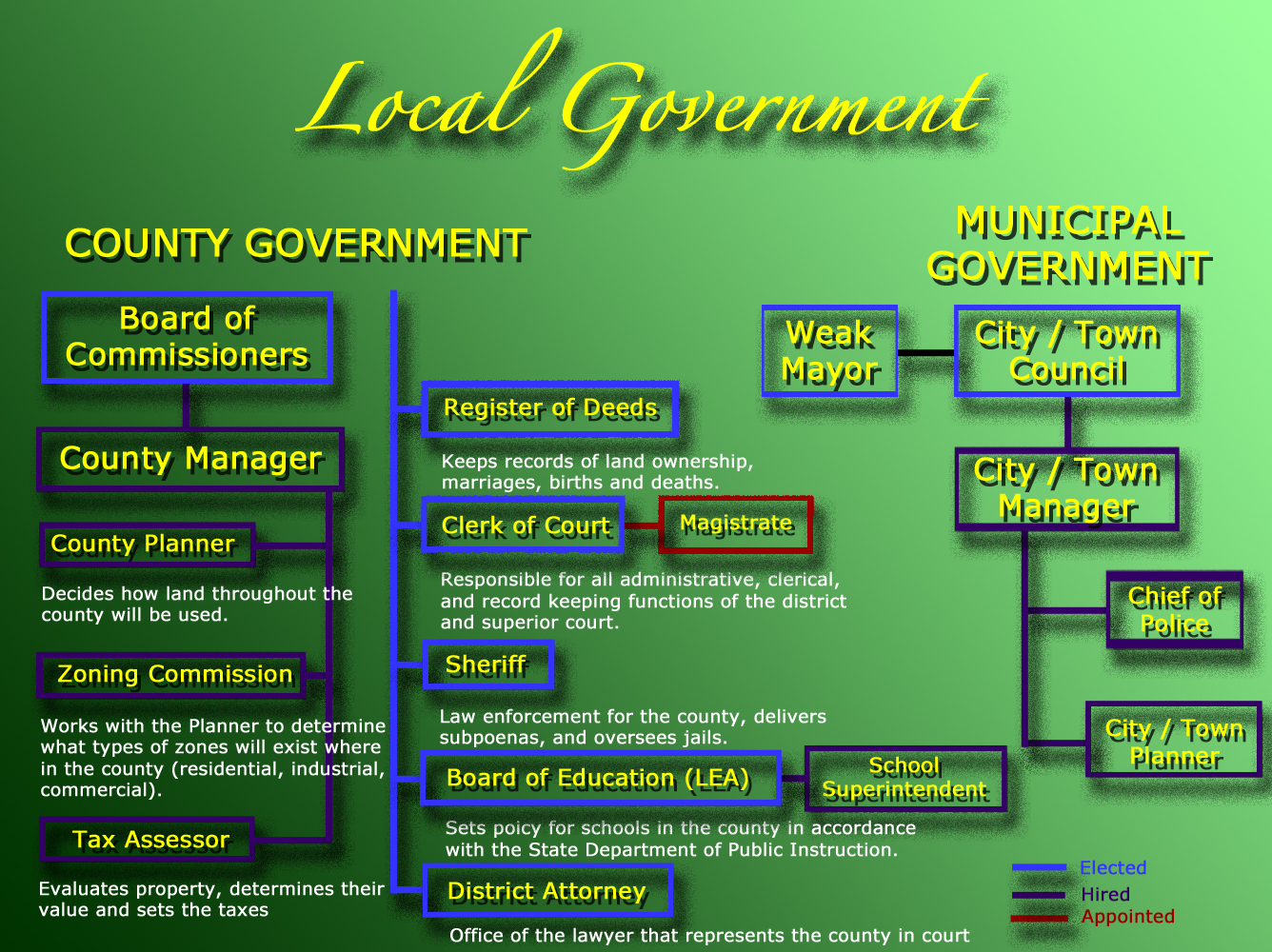
In addition, the local governments and both the county and municipal level have an executive who is tasked with enforcing and carrying out the ordinances created by local legislatures.
Study Tools
Online Textbook Resources

These pages contain the links to the online content for student practice. It includes Chapter Overviews, Web Activities, Self-Check Quizzes, ePuzzles and Games, Vocabulary Flashcards, Charts in Motion (to accompany diagrams in the textbook), and Interactive Graphic Organizers.
- Chapter 7 Student Center: The Executive Branch
Vocabulary
Link to Quizlet! Vocabulary is the key to understanding any subject. Once you can break down the barrier of language the ideas and concepts are wide open. Here you can find the vocabulary for the unit to practice by using online flash cards and by practicing online generated vocabulary quizzes.
-
Practice your vocabulary for Unit 3B by trying this quiz of the unit's vocabulary.
- Unit 3B Vocabulary Quiz on Quizlet
When you get to the Quizlet Quiz page, you can adjust what type of quiz to take by using the check boxes on the right.
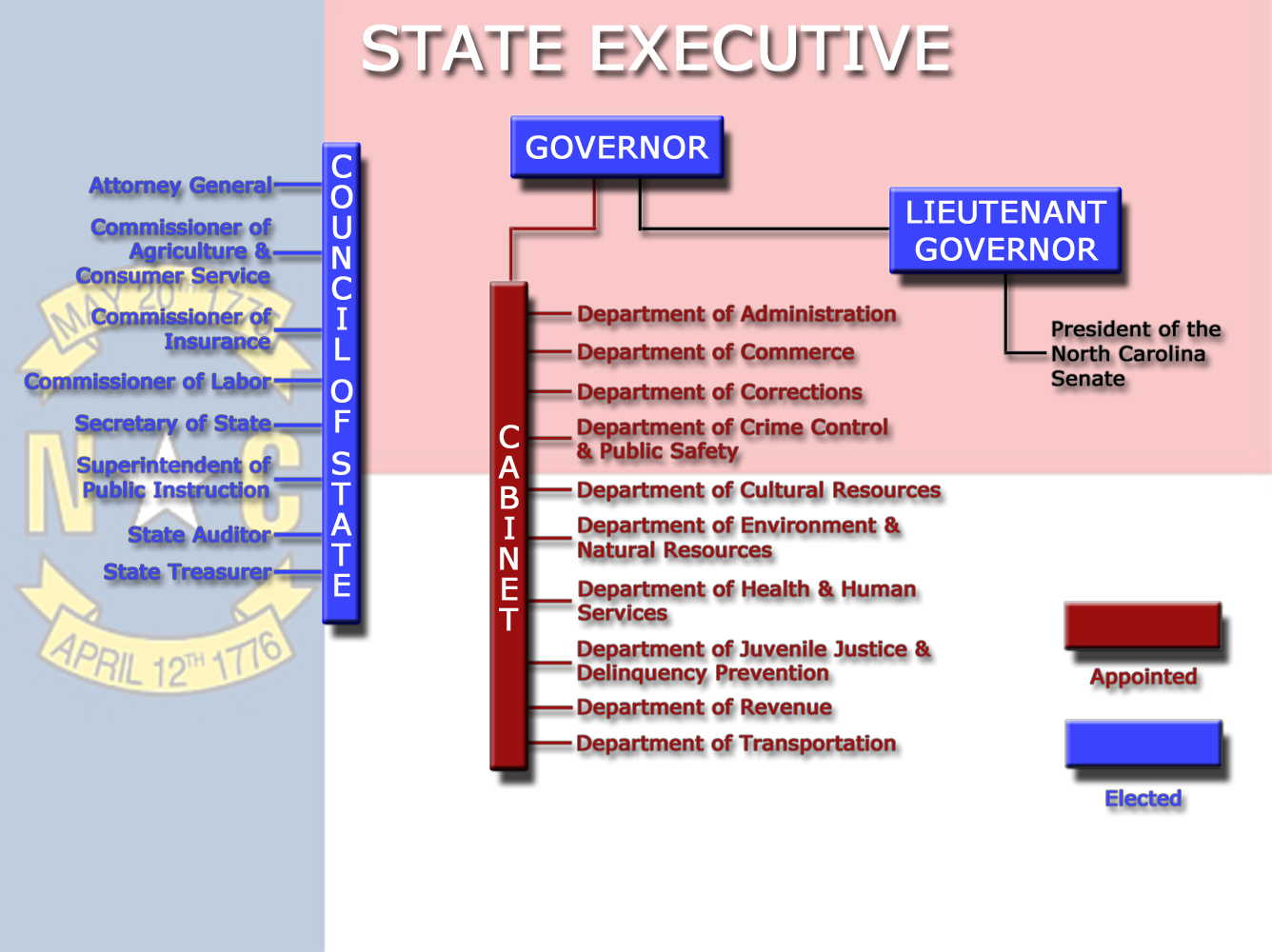
State Executive Infographic
This Infographic diagrams the Executive Branch on the State Level. You are responsible for each item on this chart. Click on the image below to open it full screen in a new window.
County & Municipal Executive Infographic
This Infographic diagrams the Executive Branch on the County and Municipal (City or Town) Level. You are responsible for each item on this chart. Click on the image below to open it full screen in a new window.
The President and the Vice President
This presentation accompanies section 7.1 and gives just some basic information about the qualifications and privileges of the president and vice-president.
Roles of the President
This presentation accompanies section 7.2 in the textbook and contains information about the roles of the president.
Foreign Policy
Foreign Policy is a nation's plan for relating with other nations, hopefully in peace, but in preparation for war. This presentation accompanies section 7.3 of the textbook dealing with US Foreign Policy.
Presidential Helpers
The president could not possibly do all the tasks of the executive branch on his own - there is an army of workers, under the direction of the president, who carry out the work of the executive branch. This presentation, to accompany section 7.4, begins to describe how the executive bureaucracy assist the president.
State Executive
As the nation is made up of states, each has its own government, its own Executive Branch. Here is some basic information about the Governor, Lieutenant Governor, Cabinet, and Council of State. It goes along with section 13.2 in the textbook. Please note, as the General Assembly continues to change some of these position, this information may become out of date.
Videos
Crash Course #11: Presidential Power #1
From the publisher:
Craig looks at the expressed powers of the President of the United States - that is the ones you can find in the Constitution. From appointing judges and granting pardons, to vetoing laws and acting as the nation’s chief diplomat on foreign policy, the Commander in Chief is a pretty powerful person, but actually not as powerful as you might think. The Constitution also limits presidential powers to maintain balance among the three branches of government. Next week we'll talk about the president's powers NOT mentioned in the Constitution - implied powers.
Crash Course #12: Presidential Power #2
From the publisher:
Craig continues our conversation on presidential powers by looking at those NOT found in the Constitution - implied or inherent powers. We’ll talk about how the president uses his or her power to negotiate executive agreements, recommend legislative initiatives, instate executive orders, impound funds, and claim executive privilege in order to get things done. Implied powers are kind of tough to tack down, as they aren’t really powers until they’re asserted, but once the they are, most subsequent presidents chose not to give them up. So we’ll try to cover those we’ve seen so far and talk a little bit about reactions to these sometimes controversial actions from the other branches of Congress.
Crash Course #13: Congressional Delegation
From the publisher:
Craig Benzine teaches you about delegation, and informal powers. What are all these federal agencies about? Well, the president has a lot of stuff to do as the chief executive, and as much as Americans like to talk about personal responsibility, the president can't really do all this stuff alone. Because it's a huge job! Same deal with Congress. So, they delegate authority. This is where all the government agencies and stuff come from. The Congress creates them to actually get around to enforcing laws. You'll learn about stuff like OSHA, and the FDA, and maybe even the FCC. Although you hear an occasional complaint about bureaucracies and such, the business of government wouldn't get done without agencies and delegation.
Crash Course #14: How Presidents Govern
From the publisher:
Craig Benzine talks about how the president gets things done. Filling the role of the executive branch is a pretty big job - much too big for just one person. It's so big that the president employs an entire federal bureaucracy! Today, we’re just going to focus on those closest to the president, like the vice president, the Cabinet, and the Executive Office of the President. We’ll figure out which strategy is most useful in helping the president make things happen and we’ll discuss the controversy around the president’s gradual increase in power. Oh, and as many of you noticed - last episode eagle got off too easy. Let’s see if we can make it up to you.
Crash Course #15: Bureaucracy Basics
From the publisher:
Craig Benzine discuses bureaucracies. Bureaucracies tend to be associated with unintelligible rules and time-wasting procedures, but they play an important, though controversial, role in governing. From the FDA to the EPA, these agencies were established to help the government manage and carry out laws much more efficiently - to bring the rule making and enforcement closer to the experts. But the federal bureaucracy (which is part of the executive branch) has a lot of power and sometimes acts likes Congress in creating regulations and like the courts through administrative adjudications. It's all a bit problematic for that whole "separation of powers" thing. So we'll talk about that too, and the arguments for and against increased federal bureaucracy.
Crash Course #16: Types of Bureaucracies
From the publisher:
Craig Benzine breaks down the different types of bureaucracies. I mean sure, they’re all part of the executive branch, but some work more directly with the president than others. Some bureaucracies exist solely to independently regulate industry whereas others are expected to operate like corporations and make a profit. And on top of all that, some of these agencies have sub-agencies! It can all get pretty complicated, so we’ll try to discuss some of the most significant agencies out there and the ones you hear a lot about on the news. We’ll talk about how they seem to have steadily gained more and more power, and of course, we’ll talk about what all the agencies are for in the first place!
Crash Course #17: Controlling Bureaucracies
From the publisher:
Craig Benzine tells you how we keep bureaucracy in check. So we've spent the last few episodes telling you all about what bureaucracies are and why they are formed. And throughout we've hinted about this ever-expanding power within the executive branch. So today, we're going to finish our discussion of bureaucracy by looking at methods the other branches of government use to manage this power. From watch-dog organizations to reporting requirements there has been quite a bit of legislation passed aimed at taming the bureaucracy.
Video Link: Annenberg Media - Learner.org
- Democracy
in America - "The Modern Presidency: Tools of Power"
To get to this program, in the window that open, scroll down to the title "7. The Modern Presidency: Tools of Power" and click the "VoD" icon on the right.
From the website: "This program shows that the American Presidency has been transformed since the 1930s. Today, presidents are overtly active in the legislative process: they use the media to appeal directly to the people and they exercise leadership over an "institutional presidency" with thousands of aides."
- Democracy
in America - "Bureaucracy: A Controversial Necessity"
To get to this program, in the window that opens, scroll down to the title "8. Bureaucracy: A Controversial Necessity" and click the "VoD" icon on the right.
From the website: "This program reveals how the American bureaucracy delivers significant services directly to the people, how it has expanded in response to citizen demands for increased government services, and how bureaucrats sometimes face contradictory expectations that are difficult to satisfy."
- The
Consitution: That Delicate Balance - "War Powers and
Covert Action"
To get to this program, in the window that opens, scroll down to the title "2. War Powers and Covert Action" and click the "VoD" icon on the right.
From the website: "If the president, as commander in chief, decides to declare war, can Congress restrain him? Debating the issue are Gerald Ford, former CIA deputy director Bobby Inman, former secretary of state Edmund Muskie, and others."
Links
- "Executive Command"
In this game you are elected President and have the daunting task of working with Congress, dealing with new bills, and contending with international crises. Can you handle the rigorous schedule and demands of running a nation?
Executive Branch
- Office
of the President - whitehouse.gov
This is the official website of the President. It contains all news released by the White House offices and links to information and agencies related to the work of the Executive Branch.
- The
Cabinet
From the website:
"The tradition of the Cabinet dates back to the beginnings of the Presidency itself. Established in Article II, Section 2, of the Constitution, the Cabinet's role is to advise the President on any subject he may require relating to the duties of each member's respective office."The Cabinet includes the Vice President and the heads of 15 executive departments — the Secretaries of Agriculture, Commerce, Defense, Education, Energy, Health and Human Services, Homeland Security, Housing and Urban Development, Interior, Labor, State, Transportation, Treasury, and Veterans Affairs, as well as the Attorney General."
- United
States Secret Service
Originally created in 1865 to fight counterfeiting of US Currency, it's responsibility has grown to include protecting the President, Presidential candidates, and investigating suspicious person in the interest of national security.